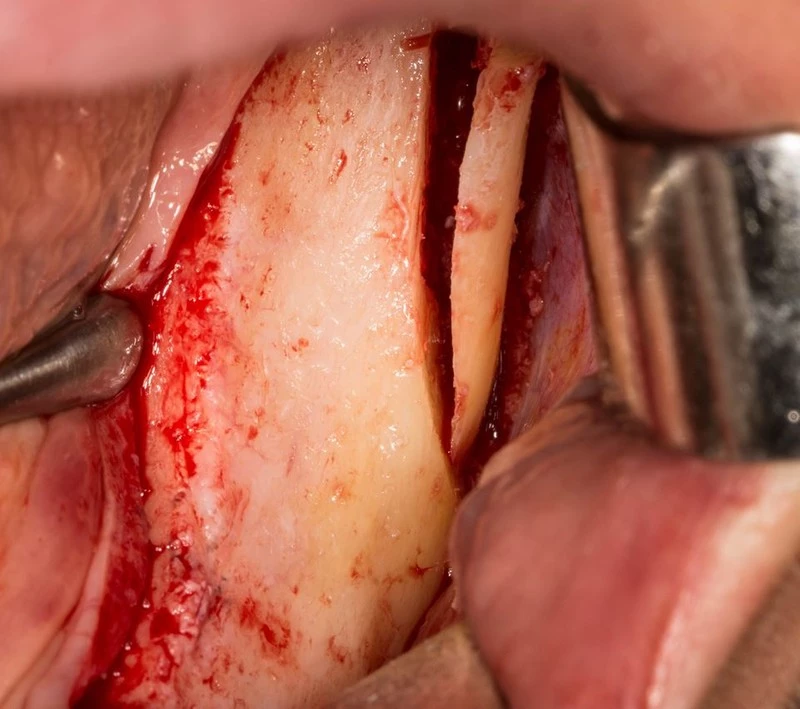
The Best Device For Ridge Expansion
Alveolar ridge expansion is a demanding surgical procedure in modern implantology. It is generally understood that osteotomies in narrow ridge should be as conservative as possible without comprising control on the implant or deviation from placement axis. Choosing the right device for ridge expansion (also known as ridge splitting) is dependent on several factors including 3D gap extension, type and size of implants, type of proposed prosthesis as well as type, technique and material of graft. In older era, bone splitting was done with chisels with/without bone grafting in the edentulous areas; choosing the graft was dependent on alveolar bone width, and bone must be spread equally on all sides of the alveolar ridge for adequate blood supply.

In modern practice, there are other electronic devices used for ridge splitting; the advances of such tools came after the introduction of root-form implants that need minimal access to the bone to undergo osteo-integration and long-term stability. The common trends in such devices are the piezoelectric or ultrasonic surgical devices and Lasers. Their mechanism relies on cracking the bone with a greenstick fracture to displace the cortical bone plate while creating a space for the implant to dwell in. The ultrasonic bone surgery can be performed with non-cutting drills only to facilitate ridge splitting in atrophic areas and to condense trabecular bone if needed.
Osteotomes are new devices with lower resonance frequency capable to perform ridge splitting without causing undesired fracture lines on the cortical plates. Their use has shown much lesser bone loss and least heat generation, while bone expansion was completed in a gradual manner without losing the integrity of bone or the surrounding soft tissues. Osteotomes are normally attached to hand piece and transmit electrical or magnetic shock waves through their tip to create the desired bone fine cutting.

Piezoelectric devices are currently used on a large scale for crest ridge expansion as they have the advantage of being atraumatic to mucosa, nerves and blood vessels in addition to providing better bone/soft-tissue healing. They serve best at areas with cancellous bone in edentulous ridge where selective bone cutting need to be carried out. They normally hold oscillating tips for saline irrigation that gives cleaner surgical field and enhanced visibility. They are now considered as the most reliable alternative to the conventional chisel and mallet tools; with the advantages of allowing for equal distribution of forces and adequate site preparation while preventing excessive bone injury.